The first discovered probiotic was a certain strain of bacillus in Bulgarian yogurt, called Lactobacillus bulgaricus. The discovery was made in 1905 by Bulgarian physician and microbiologist Stamen Grigorov.
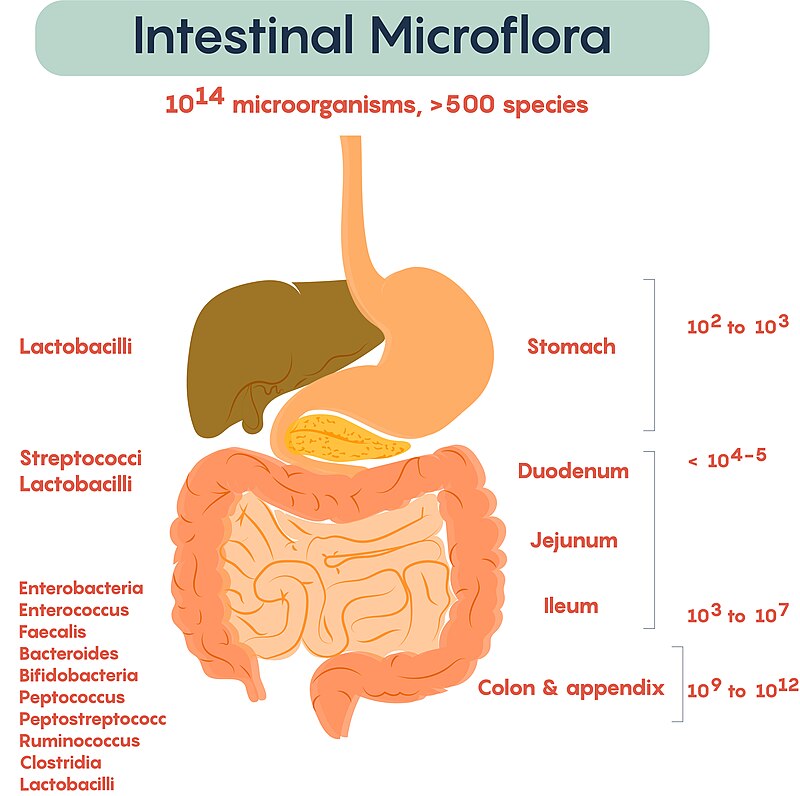
Probiotics are live microorganisms, primarily bacteria and yeast, that confer health benefits to the host when consumed in adequate amounts. They are commonly known as “good” or “friendly” bacteria because they promote a healthy balance of microflora in the digestive system.
Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (E. coli Nissle 1917) is a specific strain of the bacterium Escherichia coli that has been extensively studied and is known for its probiotic properties.
Unlike many other strains of E. coli that can cause illness, E. coli Nissle 1917 is considered safe and beneficial for human health.
Some key points about E. coli Nissle 1917: Kinds of Probiotic
Gut Health: E. coli Nissle 1917 is often used to promote gut health. It is thought to have positive effects on the balance of the gut microbiota, which plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall immune function.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Research suggests that E. coli Nissle 1917 may be beneficial in the management of certain gastrointestinal disorders, such as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like ulcerative colitis.
Immune Modulation: The strain has been shown to modulate the immune system, potentially helping to regulate the body’s immune responses.
Medical Use: E. coli Nissle 1917 has been used in the development of certain medical products, such as probiotic supplements and pharmaceuticals targeted at gastrointestinal health.
The strain was originally isolated by German physician Dr. Alfred Nissle in 1917. It has since been studied for its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in the context of gastrointestinal and immune health.
Kinds of Probiotic
Probiotics come in various strains, and different strains may offer distinct health benefits. Here are some common types of probiotics and their associated strains:
- Lactobacillus genus:
- L. acidophilus: Found in the small intestine and vagina; it may help with digestion and is commonly found in yogurt.
- L. casei: Supports the immune system and is found in fermented foods like dairy products.
- L. plantarum: Resides in the digestive tract and may help with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other digestive issues.
- L. rhamnosus: Known for its role in promoting gut health and preventing diarrhea, it’s found in dairy products.
- Bifidobacterium genus:
- B. bifidum: Abundant in the colon, it aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
- B. breve: Plays a role in colon health and supports the immune system.
- B. longum: Supports the immune system and contributes to the digestion of complex carbohydrates.
- B. lactis: Found in dairy products, it aids in the digestion of lactose and supports the immune system.
- Saccharomyces boulardii:
- This yeast probiotic is known for its ability to prevent and treat diarrhea associated with antibiotic use or infections. It’s not a bacteria but is often included in discussions about probiotics.
- Enterococcus genus:
- E. faecium: Some strains of Enterococcus faecium are used as probiotics, contributing to gut health.
- Streptococcus genus:
- S. thermophilus: Used in the fermentation of yogurt and may contribute to gut health.
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) Nissle 1917:
- A strain of E. coli that has probiotic properties and is used to treat various gastrointestinal conditions.
I have spent the last 20 years researching and training in the following areas because I am passionate about assisting my clients in achieving optimal health and well-being:
Electro Acupuncture, Biological pathways, Cellular Membranes, Vagus Nerve, Leaky gut syndrome, Western Herbalist, Natural Remedies, Herbal Medications, Mayan Medicines, Parasites.
Herbal medicine (also called herbalism, phytomedicine, or phytotherapy) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are the basis of traditional medicine.



 Joan Cass
Joan Cass Joan Cass
Joan Cass